Which Organelles Are Found Only In Animal Cells
Fauna Prison cell Structure
Fauna cells are typical of the eukaryotic prison cell, enclosed by a plasma membrane and containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Unlike the eukaryotic cells of plants and fungi, animal cells do non have a cell wall. This feature was lost in the distant past by the single-celled organisms that gave rise to the kingdom Animalia. Nearly cells, both animal and constitute, range in size betwixt 1 and 100 micrometers and are thus visible only with the assist of a microscope.
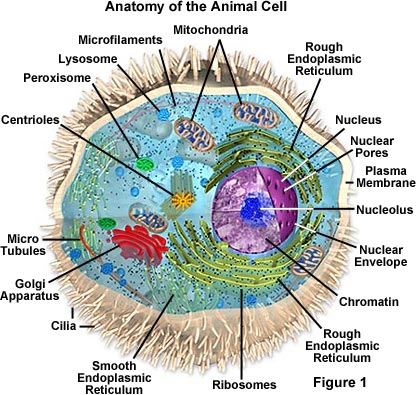
The lack of a rigid cell wall allowed animals to develop a greater diversity of cell types, tissues, and organs. Specialized cells that formed fretfulness and muscles�tissues impossible for plants to evolve�gave these organisms mobility. The ability to movement near by the use of specialized muscle tissues is a hallmark of the animal world, though a few animals, primarily sponges, do not possess differentiated tissues. Notably, protozoans locomote, but it is only via nonmuscular means, in effect, using cilia, flagella, and pseudopodia.
The fauna kingdom is unique among eukaryotic organisms because most animal tissues are spring together in an extracellular matrix by a triple helix of protein known as collagen. Plant and fungal cells are bound together in tissues or aggregations past other molecules, such equally pectin. The fact that no other organisms utilize collagen in this manner is one of the indications that all animals arose from a mutual unicellular ancestor. Bones, shells, spicules, and other hardened structures are formed when the collagen-containing extracellular matrix between animal cells becomes calcified.
Animals are a big and incredibly diverse grouping of organisms. Making upwardly well-nigh 3-quarters of the species on Earth, they run the gamut from corals and jellyfish to ants, whales, elephants, and, of course, humans. Being mobile has given animals, which are capable of sensing and responding to their environs, the flexibility to adopt many unlike modes of feeding, defense, and reproduction. Unlike plants, however, animals are unable to manufacture their own food, and therefore, are always directly or indirectly dependent on plant life.
Virtually animate being cells are diploid, pregnant that their chromosomes exist in homologous pairs. Unlike chromosomal ploidies are also, however, known to occasionally occur. The proliferation of brute cells occurs in a variety of means. In instances of sexual reproduction, the cellular process of meiosis is showtime necessary and so that haploid daughter cells, or gametes, tin can exist produced. Two haploid cells and then fuse to form a diploid zygote, which develops into a new organism equally its cells divide and multiply.
The earliest fossil testify of animals dates from the Vendian Period (650 to 544 million years ago), with coelenterate-blazon creatures that left traces of their soft bodies in shallow-water sediments. The first mass extinction ended that menstruum, only during the Cambrian Catamenia which followed, an explosion of new forms began the evolutionary radiations that produced most of the major groups, or phyla, known today. Vertebrates (animals with backbones) are not known to have occurred until the early Ordovician Period (505 to 438 million years ago).
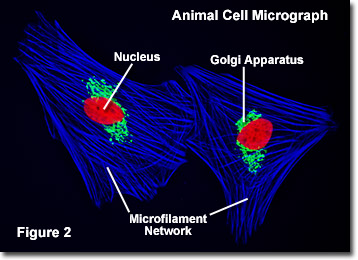
Cells were discovered in 1665 past British scientist Robert Hooke who first observed them in his rough (past today's standards) seventeenth century optical microscope. In fact, Hooke coined the term "prison cell", in a biological context, when he described the microscopic structure of cork similar a tiny, blank room or monk's cell. Illustrated in Figure two are a pair of fibroblast deer skin cells that have been labeled with fluorescent probes and photographed in the microscope to reveal their internal structure. The nuclei are stained with a red probe, while the Golgi appliance and microfilament actin network are stained light-green and blue, respectively. The microscope has been a fundamental tool in the field of cell biology and is often used to detect living cells in civilization. Use the links below to obtain more than detailed information nearly the diverse components that are plant in animal cells.
-
Centrioles - Centrioles are self-replicating organelles made upwardly of 9 bundles of microtubules and are found only in creature cells. They appear to help in organizing jail cell partitioning, only aren't essential to the process.
-
Cilia and Flagella - For single-celled eukaryotes, cilia and flagella are essential for the locomotion of individual organisms. In multicellular organisms, cilia function to motion fluid or materials past an immobile cell as well as moving a cell or group of cells.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum - The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of sacs that manufactures, processes, and transports chemic compounds for use inside and outside of the cell. It is continued to the double-layered nuclear envelope, providing a pipeline betwixt the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
-
Endosomes and Endocytosis - Endosomes are membrane-bound vesicles, formed via a complex family of processes collectively known as endocytosis, and institute in the cytoplasm of virtually every animate being cell. The basic mechanism of endocytosis is the reverse of what occurs during exocytosis or cellular secretion. Information technology involves the invagination (folding inward) of a prison cell's plasma membrane to surround macromolecules or other matter diffusing through the extracellular fluid.
-
Golgi Apparatus - The Golgi appliance is the distribution and shipping department for the prison cell's chemical products. It modifies proteins and fats built in the endoplasmic reticulum and prepares them for consign to the outside of the prison cell.
-
Intermediate Filaments - Intermediate filaments are a very broad class of fibrous proteins that play an important part as both structural and functional elements of the cytoskeleton. Ranging in size from 8 to 12 nanometers, intermediate filaments function as tension-bearing elements to help maintain cell shape and rigidity.
-
Lysosomes - The main function of these microbodies is digestion. Lysosomes intermission down cellular waste material products and debris from outside the cell into uncomplicated compounds, which are transferred to the cytoplasm equally new cell-building materials.
-
Microfilaments - Microfilaments are solid rods made of globular proteins called actin. These filaments are primarily structural in function and are an important component of the cytoskeleton.
-
Microtubules - These straight, hollow cylinders are found throughout the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells (prokaryotes don't have them) and carry out a variety of functions, ranging from transport to structural support.
-
Mitochondria - Mitochondria are oblong shaped organelles that are constitute in the cytoplasm of every eukaryotic cell. In the fauna cell, they are the primary power generators, converting oxygen and nutrients into energy.
-
Nucleus - The nucleus is a highly specialized organelle that serves as the data processing and administrative heart of the prison cell. This organelle has two major functions: information technology stores the prison cell'south hereditary fabric, or DNA, and it coordinates the prison cell's activities, which include growth, intermediary metabolism, poly peptide synthesis, and reproduction (cell segmentation).
-
Peroxisomes - Microbodies are a diverse grouping of organelles that are found in the cytoplasm, roughly spherical and bound by a single membrane. In that location are several types of microbodies only peroxisomes are the most common.
-
Plasma Membrane - All living cells have a plasma membrane that encloses their contents. In prokaryotes, the membrane is the inner layer of protection surrounded by a rigid jail cell wall. Eukaryotic animal cells accept only the membrane to contain and protect their contents. These membranes also regulate the passage of molecules in and out of the cells.
-
Ribosomes - All living cells incorporate ribosomes, tiny organelles equanimous of approximately 60 percentage RNA and xl percent protein. In eukaryotes, ribosomes are made of four strands of RNA. In prokaryotes, they consist of three strands of RNA.
In addition the optical and electron microscope, scientists are able to use a number of other techniques to probe the mysteries of the animal cell. Cells tin be disassembled past chemical methods and their individual organelles and macromolecules isolated for report. The process of cell fractionation enables the scientist to prepare specific components, the mitochondria for instance, in big quantities for investigations of their limerick and functions. Using this approach, jail cell biologists have been able to assign various functions to specific locations within the cell. However, the era of fluorescent proteins has brought microscopy to the forefront of biological science by enabling scientists to target living cells with highly localized probes for studies that don't interfere with the delicate balance of life processes.
Back TO Cell STRUCTURE Dwelling house
BACK TO FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY OF CELLS
Questions or comments? Send us an email.
© 1995-2022 by Michael W. Davidson and The Florida State Academy. All Rights Reserved. No images, graphics, software, scripts, or applets may be reproduced or used in any way without permission from the copyright holders. Use of this website means yous concur to all of the Legal Terms and Weather condition set up forth by the owners.
This website is maintained by our
Graphics & Web Programming Team
in collaboration with Optical Microscopy at the
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory.
Last modification: Friday, November 13, 2015 at 02:xviii PM
Access Count Since October 1, 2000: 6358683
Microscopes provided past:
Source: https://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/animalcell.html
Posted by: nelsonbehateror.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Which Organelles Are Found Only In Animal Cells"
Post a Comment